Finding fossils takes a combination of skill and luck. You have to be looking in the right place and have some idea of how to distinguish those precious pieces of prehistoric life from all the rock surrounding it. But that’s not all. How the sun hits stone, where your eyes fall along the outcrop, and even where you stop to take a leak can make all the difference between finding something amazing and passing it by. And that’s just in the field. Museum collections hold petrified trails of bread crumbs, too, leading to forgotten places whose fossiliferous potential hasn’t been realized.
Sometime in the late 70s or early 80s, geology student Thomas Schröter was hiking through the red rocks of Algarve, Portugal when he spotted some fossil bone. They didn’t relate to the thesis he was working on, but he picked them up anyway. While not especially remarkable, the scraps nevertheless made the customary transition from field to museum collection and were later appraised as those of a metoposaur – salamander-like amphibians that could get up to 10 feet long and lived a lifestyle one of my professors once called “crocodiling before there were crocodiles.”
These enormous amphibians were, and are, anything but rare. They’re among the most common fossils found in the 237-201 million year old rock representing Late Triassic time, sometimes clustered together in dense bonebed where they died en masse. And as paleontologists Stephen Brusatte, Richard Butler, Octávio Mateus, and Sébastien Steyer found when they relocated the Algarve site in 2009 after reading a short description of the fragments plucked from the site, Schröter had discovered another such graveyard.

There’s more in the Algarve bonebed than has yet been excavated and prepared. So far, however, Brusatte and colleagues have uncovered multiple skulls and bones from the chests of these aquatic ambush predators. And while these remains are similar to those of other Metoposaurus found elsewhere in Europe, they’re different enough to justify establishing a new species – Metoposaurus algarvensis.
What brought so many Metoposaurus together to die isn’t clear. At this point, the researchers write, it’s unknown whether they died in the place they were entombed or their remains were washed in from elsewhere. But seasonal droughts could have played a role.
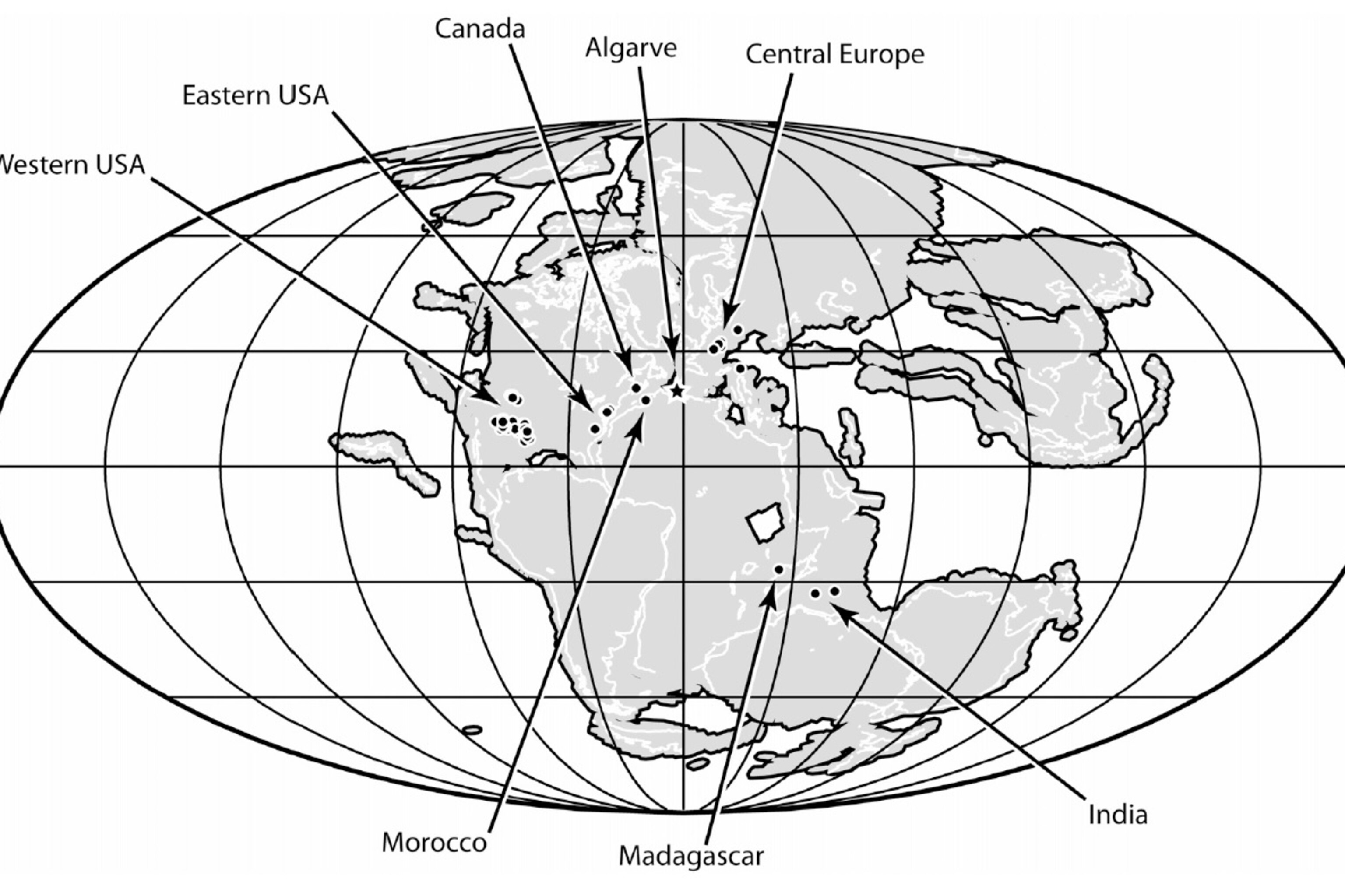
Algarve was much closer to the equator in the Triassic than today, scorched in dry seasons and doused by the return of the monsoons. Perhaps the unfortunate Metoposaurus were pushed together into an ever-shrinking water source, baked to death before rains returned to bury them.
Regardless of the reason for their death, though, the fossils are part of a metoposaur band that ran across the middle of Pangaea, the only outliers being a cluster in prehistoric India and Madagascar. Future finds will alter this picture to greater or lesser degrees, but it may be that metoposaurs thrived in hot, highly-seasonal environments where early dinosaurs stayed small and croc cousins ruled while different predators waited along the shores of higher-latitude habitats. The only way to find out more is to keep digging.
Reference:
Brusatte, S., Butler, R., Mateus, O., Steyer, S. 2015. A new species of Metoposaurus from the Late Triassic of Portugal and comments on the systematics and biogeography of metoposaurid temnospondyls. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi: 10.1080/2724634.2014.912988
Related Topics
Go Further
Animals
- Orangutan seen using plants to heal wound for first timeOrangutan seen using plants to heal wound for first time
- What La Palma's 'lava tubes' tell us about life on other planetsWhat La Palma's 'lava tubes' tell us about life on other planets
- This fungus turns cicadas into zombies who procreate—then dieThis fungus turns cicadas into zombies who procreate—then die
- How can we protect grizzlies from their biggest threat—trains?How can we protect grizzlies from their biggest threat—trains?
- This ‘saber-toothed’ salmon wasn’t quite what we thoughtThis ‘saber-toothed’ salmon wasn’t quite what we thought
Environment
- What La Palma's 'lava tubes' tell us about life on other planetsWhat La Palma's 'lava tubes' tell us about life on other planets
- How fungi form ‘fairy rings’ and inspire superstitionsHow fungi form ‘fairy rings’ and inspire superstitions
- Your favorite foods may not taste the same in the future. Here's why.Your favorite foods may not taste the same in the future. Here's why.
- Are the Great Lakes the key to solving America’s emissions conundrum?Are the Great Lakes the key to solving America’s emissions conundrum?
- The world’s historic sites face climate change. Can Petra lead the way?The world’s historic sites face climate change. Can Petra lead the way?
History & Culture
- Meet the ruthless king who unified the Kingdom of Hawai'iMeet the ruthless king who unified the Kingdom of Hawai'i
- Hawaii's Lei Day is about so much more than flowersHawaii's Lei Day is about so much more than flowers
- When treasure hunters find artifacts, who gets to keep them?When treasure hunters find artifacts, who gets to keep them?
Science
- Why ovaries are so crucial to women’s health and longevityWhy ovaries are so crucial to women’s health and longevity
- Orangutan seen using plants to heal wound for first timeOrangutan seen using plants to heal wound for first time
- Should you be concerned about bird flu in your milk?Should you be concerned about bird flu in your milk?
Travel
- 5 of Uganda’s most magnificent national parks
- Paid Content
5 of Uganda’s most magnificent national parks - On this Croatian peninsula, traditions are securing locals' futuresOn this Croatian peninsula, traditions are securing locals' futures
- Are Italy's 'problem bears' a danger to travellers?Are Italy's 'problem bears' a danger to travellers?
- How to navigate Nantes’ arts and culture scene
- Paid Content
How to navigate Nantes’ arts and culture scene
